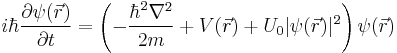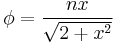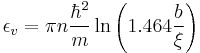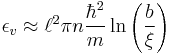Bose–Einstein condensate
A Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) is a state of matter of a dilute gas of weakly interacting bosons confined in an external potential and cooled to temperatures very near absolute zero (0 K or −273.15 °C[1]). Under such conditions, a large fraction of the bosons occupy the lowest quantum state of the external potential, at which point quantum effects become apparent on a macroscopic scale.
This state of matter was first predicted by Satyendra Nath Bose and Albert Einstein in 1924–25. Bose first sent a paper to Einstein on the quantum statistics of light quanta (now called photons). Einstein was impressed, translated the paper himself from English to German and submitted it for Bose to the Zeitschrift für Physik, which published it. Einstein then extended Bose's ideas to material particles (or matter) in two other papers.[2]
Seventy years later, the first gaseous condensate was produced by Eric Cornell and Carl Wieman in 1995 at the University of Colorado at Boulder NIST-JILA lab, using a gas of rubidium atoms cooled to 170 nanokelvin (nK) [3] (1.7×10−7 K). For their achievements Cornell, Wieman, and Wolfgang Ketterle at MIT received the 2001 Nobel Prize in Physics.[4] In November 2010 the first photon BEC was observed.[5]
The slowing of atoms by the use of cooling apparatus produced a singular quantum state known as a Bose condensate or Bose–Einstein condensate. This phenomenon was predicted in 1925 by generalizing Satyendra Nath Bose's work on the statistical mechanics of (massless) photons to (massive) atoms. (The Einstein manuscript, once believed to be lost, was found in a library at Leiden University in 2005.[6]) The result of the efforts of Bose and Einstein is the concept of a Bose gas, governed by Bose–Einstein statistics, which describes the statistical distribution of identical particles with integer spin, now known as bosons. Bosonic particles, which include the photon as well as atoms such as helium-4, are allowed to share quantum states with each other. Einstein demonstrated that cooling bosonic atoms to a very low temperature would cause them to fall (or "condense") into the lowest accessible quantum state, resulting in a new form of matter.
This transition occurs below a critical temperature, which for a uniform three-dimensional gas consisting of non-interacting particles with no apparent internal degrees of freedom is given by:
where:
-
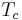
is the critical temperature, 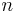
is the particle density, 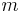
is the mass per boson, 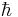
is the reduced Planck constant, 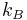
is the Boltzmann constant, and 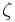
is the Riemann zeta function; 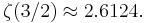 (sequence A078434 in OEIS)
(sequence A078434 in OEIS)
Contents |
Einstein's argument
Consider a collection of N noninteracting particles, which can each be in one of two quantum states,  and
and 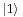 . If the two states are equal in energy, each different configuration is equally likely.
. If the two states are equal in energy, each different configuration is equally likely.
If we can tell which particle is which, there are 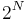 different configurations, since each particle can be in
different configurations, since each particle can be in 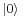 or
or 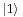 independently. In almost all of the configurations, about half the particles are in
independently. In almost all of the configurations, about half the particles are in 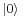 and the other half in
and the other half in 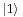 . The balance is a statistical effect: the number of configurations is largest when the particles are divided equally.
. The balance is a statistical effect: the number of configurations is largest when the particles are divided equally.
If the particles are indistinguishable, however, there are only N+1 different configurations. If there are K particles in state 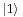 , there are N − K particles in state
, there are N − K particles in state 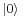 . Whether any particular particle is in state
. Whether any particular particle is in state 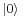 or in state
or in state 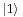 cannot be determined, so each value of K determines a unique quantum state for the whole system. If all these states are equally likely, there is no statistical spreading out; it is just as likely for all the particles to sit in
cannot be determined, so each value of K determines a unique quantum state for the whole system. If all these states are equally likely, there is no statistical spreading out; it is just as likely for all the particles to sit in 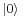 as for the particles to be split half and half.
as for the particles to be split half and half.
Suppose now that the energy of state 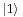 is slightly greater than the energy of state
is slightly greater than the energy of state 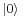 by an amount E. At temperature T, a particle will have a lesser probability to be in state
by an amount E. At temperature T, a particle will have a lesser probability to be in state 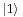 by exp(−E/T). In the distinguishable case, the particle distribution will be biased slightly towards state
by exp(−E/T). In the distinguishable case, the particle distribution will be biased slightly towards state 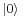 and the distribution will be slightly different from half and half. But in the indistinguishable case, since there is no statistical pressure toward equal numbers, the most likely outcome is that most of the particles will collapse into state
and the distribution will be slightly different from half and half. But in the indistinguishable case, since there is no statistical pressure toward equal numbers, the most likely outcome is that most of the particles will collapse into state 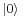 .
.
In the distinguishable case, for large N, the fraction in state 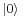 can be computed. It is the same as flipping a coin with probability proportional to p = exp(−E/T) to land tails. The probability to land heads is 1/(1 + p), which is a smooth function of p, and thus of the energy.
can be computed. It is the same as flipping a coin with probability proportional to p = exp(−E/T) to land tails. The probability to land heads is 1/(1 + p), which is a smooth function of p, and thus of the energy.
In the indistinguishable case, each value of K is a single state, which has its own separate Boltzmann probability. So the probability distribution is exponential:
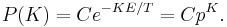
For large N, the normalization constant C is (1 − p). The expected total number of particles not in the lowest energy state, in the limit that 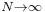 , is equal to
, is equal to 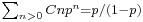 . It does not grow when N is large, it just approaches a constant. This will be a negligible fraction of the total number of particles. So a collection of enough Bose particles in thermal equilibrium will mostly be in the ground state, with only a few in any excited state, no matter how small the energy difference.
. It does not grow when N is large, it just approaches a constant. This will be a negligible fraction of the total number of particles. So a collection of enough Bose particles in thermal equilibrium will mostly be in the ground state, with only a few in any excited state, no matter how small the energy difference.
Consider now a gas of particles, which can be in different momentum states labeled 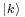 . If the number of particles is less than the number of thermally accessible states, for high temperatures and low densities, the particles will all be in different states. In this limit the gas is classical. As the density increases or the temperature decreases, the number of accessible states per particle becomes smaller, and at some point more particles will be forced into a single state than the maximum allowed for that state by statistical weighting. From this point on, any extra particle added will go into the ground state.
. If the number of particles is less than the number of thermally accessible states, for high temperatures and low densities, the particles will all be in different states. In this limit the gas is classical. As the density increases or the temperature decreases, the number of accessible states per particle becomes smaller, and at some point more particles will be forced into a single state than the maximum allowed for that state by statistical weighting. From this point on, any extra particle added will go into the ground state.
To calculate the transition temperature at any density, integrate over all momentum states the expression for maximum number of excited particles p/(1 − p):
When the integral is evaluated with the factors of kB and ℏ restored by dimensional analysis, it gives the critical temperature formula of the preceding section. Therefore, this integral defines the critical temperature and particle number corresponding to the conditions of negligible chemical potential. In Bose–Einstein statistics distribution, μ is actually still nonzero for BEC's; however, μ is less than the ground state energy. Except when specifically talking about the ground state, μ can consequently be approximated for most energy or momentum states as μ ≈ 0.
Gross–Pitaevskii equation
The state of the BEC can be described by the wavefunction of the condensate 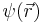 . For a system of this nature,
. For a system of this nature, 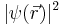 is interpreted as the particle density, so the total number of atoms is
is interpreted as the particle density, so the total number of atoms is 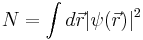
Provided essentially all atoms are in the condensate (that is, have condensed to the ground state), and treating the bosons using mean field theory, the energy (E) associated with the state 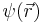 is:
is:
Minimizing this energy with respect to infinitesimal variations in 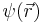 , and holding the number of atoms constant, yields the Gross-Pitaevski equation (GPE) (also a non-linear Schrödinger equation):
, and holding the number of atoms constant, yields the Gross-Pitaevski equation (GPE) (also a non-linear Schrödinger equation):
where:
-
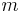
is the mass of the bosons, 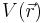
is the external potential, 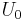
is representative of the inter-particle interactions.
The GPE provides a good description of the behavior of BEC's and is thus often applied for theoretical analysis.
Models beyond Gross–Pitaevskii
The Gross–Pitaevskii model of BEC is the physical approximation valid for certain classes of BEC's only. By construction, GPE uses the following simplifications: it assumes that interactions between condensate particles are of the contact two-body type and also it neglects anomalous contributions to self-energy.[7] These assumptions are suitable mostly for the dilute three-dimensional condensates. If one relaxes any of these assumptions, the equation for the condensate wavefunction acquires the terms containing higher-order powers of the wavefunction. Moreover, for some physical systems the amount of such terms turns out to be infinite, therefore, the equation becomes essentially non-polynomial. The examples where this could happen are the Bose-Fermi composite condensates,[8] effectively lower-dimensional condensates,[9] and dense condensates and superfluid clusters and droplets.[10]
Discovery
In 1938, Pyotr Kapitsa, John Allen and Don Misener discovered that helium-4 became a new kind of fluid, now known as a superfluid, at temperatures less than 2.17 K (the lambda point). Superfluid helium has many unusual properties, including zero viscosity (the ability to flow without dissipating energy) and the existence of quantized vortices. It was quickly realized that the superfluidity was due to partial Bose–Einstein condensation of the liquid. In fact, many of the properties of superfluid helium also appear in the gaseous Bose–Einstein condensates created by Cornell, Wieman and Ketterle (see below). Superfluid helium-4 is a liquid rather than a gas, which means that the interactions between the atoms are relatively strong; the original theory of Bose–Einstein condensation must be heavily modified in order to describe it. Bose–Einstein condensation remains, however, fundamental to the superfluid properties of helium-4. Note that helium-3, consisting of fermions instead of bosons, also enters a superfluid phase at low temperature, which can be explained by the formation of bosonic Cooper pairs of two atoms each (see also fermionic condensate).
The first "pure" Bose–Einstein condensate was created by Eric Cornell, Carl Wieman, and co-workers at JILA on June 5, 1995. They did this by cooling a dilute vapor consisting of approximately two thousand rubidium-87 atoms to below 170 nK using a combination of laser cooling (a technique that won its inventors Steven Chu, Claude Cohen-Tannoudji, and William D. Phillips the 1997 Nobel Prize in Physics) and magnetic evaporative cooling. About four months later, an independent effort led by Wolfgang Ketterle at MIT created a condensate made of sodium-23. Ketterle's condensate had about a hundred times more atoms, allowing him to obtain several important results such as the observation of quantum mechanical interference between two different condensates. Cornell, Wieman and Ketterle won the 2001 Nobel Prize in Physics for their achievements.[11] A group led by Randall Hulet at Rice University announced the creation of a condensate of lithium atoms only one month following the JILA work.[12] Lithium has attractive interactions which causes the condensate to be unstable and to collapse for all but a few atoms. Hulet and co-workers showed in a subsequent experiment that the condensate could be stabilized by the quantum pressure from trap confinement for up to about 1000 atoms.
The Bose–Einstein condensation also applies to quasiparticles in solids. A magnon in an antiferromagnet carries spin 1 and thus obeys Bose–Einstein statistics. The density of magnons is controlled by an external magnetic field, which plays the role of the magnon chemical potential. This technique provides access to a wide range of boson densities from the limit of a dilute Bose gas to that of a strongly interacting Bose liquid. A magnetic ordering observed at the point of condensation is the analog of superfluidity. In 1999 Bose condensation of magnons was demonstrated in the antiferromagnet TlCuCl3.[13] The condensation was observed at temperatures as large as 14 K. Such a high transition temperature (relative to that of atomic gases) is due to the greater density achievable with magnons and the smaller mass (roughly equal to the mass of an electron). In 2006, condensation of magnons in ferromagnets was even shown at room temperature,[14] where the authors used pumping techniques.
Velocity-distribution data graph
In the image accompanying this article, the velocity-distribution data indicates the formation of a Bose–Einstein condensate out of a gas of rubidium atoms. The false colors indicate the number of atoms at each velocity, with red being the fewest and white being the most. The areas appearing white and light blue are at the lowest velocities. The peak is not infinitely narrow because of the Heisenberg uncertainty principle: since the atoms are trapped in a particular region of space, their velocity distribution necessarily possesses a certain minimum width. This width is given by the curvature of the magnetic trapping potential in the given direction. More tightly confined directions have bigger widths in the ballistic velocity distribution. This anisotropy of the peak on the right is a purely quantum-mechanical effect and does not exist in the thermal distribution on the left. This famous graph served as the cover design for 1999 textbook Thermal Physics by Ralph Baierlein.[15]
Vortices
As in many other systems, vortices can exist in BECs. These can be created, for example, by 'stirring' the condensate with lasers, or rotating the confining trap. The vortex created will be a quantum vortex. These phenomena are allowed for by the non-linear 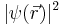 term in the GPE. As the vortices must have quantized angular momentum the wavefunction may have the form
term in the GPE. As the vortices must have quantized angular momentum the wavefunction may have the form 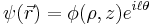 where
where 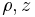 and
and 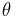 are as in the cylindrical coordinate system, and
are as in the cylindrical coordinate system, and 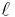 is the angular number. This is particularly likely for an axially symmetric (for instance, harmonic) confining potential, which is commonly used. The notion is easily generalized. To determine
is the angular number. This is particularly likely for an axially symmetric (for instance, harmonic) confining potential, which is commonly used. The notion is easily generalized. To determine 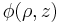 , the energy of
, the energy of 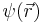 must be minimized, according to the constraint
must be minimized, according to the constraint 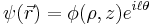 . This is usually done computationally, however in a uniform medium the analytic form
. This is usually done computationally, however in a uniform medium the analytic form
where:
-
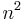
is density far from the vortex, 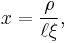
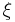
is healing length of the condensate.
demonstrates the correct behavior, and is a good approximation.
A singly charged vortex (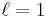 ) is in the ground state, with its energy
) is in the ground state, with its energy 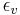 given by
given by
where:
-
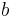
is the farthest distance from the vortex considered.
(To obtain an energy which is well defined it is necessary to include this boundary 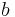 .)
.)
For multiply charged vortices (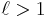 ) the energy is approximated by
) the energy is approximated by
which is greater than that of  singly charged vortices, indicating that these multiply charged vortices are unstable to decay. Research has, however, indicated they are metastable states, so may have relatively long lifetimes.
singly charged vortices, indicating that these multiply charged vortices are unstable to decay. Research has, however, indicated they are metastable states, so may have relatively long lifetimes.
Closely related to the creation of vortices in BECs is the generation of so-called dark solitons in one-dimensional BECs. These topological objects feature a phase gradient across their nodal plane, which stabilizes their shape even in propagation and interaction. Although solitons carry no charge and are thus prone to decay, relatively long-lived dark solitons have been produced and studied extensively.[16]
Attractive interactions
The experiments led by Randall Hulet at Rice University from 1995 through 2000 showed that lithium condensates with attractive interactions could stably exist, but only up to a certain critical atom number. Beyond this critical number, the attraction overwhelmed the zero-point energy of the harmonic confining potential, causing the condensate to collapse in a burst reminiscent of a supernova explosion where an explosion is preceded by an implosion. By quench cooling the gas of lithium atoms, they observed the condensate to first grow, and subsequently collapse when the critical number was exceeded.
Further experimentation on attractive condensates was performed in 2000 by the JILA team, consisting of Cornell, Wieman, and coworkers. They originally used rubidium-87, an isotope whose atoms naturally repel each other, making a more stable condensate. Their instrumentation now had better control over the condensate so experimentation was made on naturally attracting atoms of another rubidium isotope, rubidium-85 (having negative atom-atom scattering length). Through a process called Feshbach resonance involving a sweep of the magnetic field causing spin flip collisions, they lowered the characteristic, discrete energies at which the rubidium atoms bond into molecules, making their Rb-85 atoms repulsive and creating a stable condensate. The reversible flip from attraction to repulsion stems from quantum interference among condensate atoms which behave as waves.
When the JILA team raised the magnetic field strength still further, the condensate suddenly reverted back to attraction, imploded and shrank beyond detection, and then exploded, expelling off about two-thirds of its 10,000 or so atoms. About half of the atoms in the condensate seemed to have disappeared from the experiment altogether, not being seen either in the cold remnant or the expanding gas cloud.[11] Carl Wieman explained that under current atomic theory this characteristic of Bose–Einstein condensate could not be explained because the energy state of an atom near absolute zero should not be enough to cause an implosion; however, subsequent mean field theories have been proposed to explain it. The atoms that seem to have disappeared almost certainly still exist in some form, just not in a form that could be accounted for in that experiment. Most likely they formed molecules consisting of two bonded rubidium atoms[17]. The energy gained by making this transition imparts a velocity sufficient for them to leave the trap without being detected.
Current research
Compared to more commonly encountered states of matter, Bose–Einstein condensates are extremely fragile. The slightest interaction with the outside world can be enough to warm them past the condensation threshold, eliminating their interesting properties and forming a normal gas.
Nevertheless, they have proven useful in exploring a wide range of questions in fundamental physics, and the years since the initial discoveries by the JILA and MIT groups have seen an explosion in experimental and theoretical activity. Examples include experiments that have demonstrated interference between condensates due to wave-particle duality,[18] the study of superfluidity and quantized vortices, the creation of bright matter wave solitons from Bose condensates confined to one dimension, and the slowing of light pulses to very low speeds using electromagnetically induced transparency.[19] Vortices in Bose–Einstein condensates are also currently the subject of analogue gravity research, studying the possibility of modeling black holes and their related phenomena in such environments in the lab. Experimentalists have also realized "optical lattices", where the interference pattern from overlapping lasers provides a periodic potential for the condensate. These have been used to explore the transition between a superfluid and a Mott insulator,[20] and may be useful in studying Bose–Einstein condensation in fewer than three dimensions, for example the Tonks-Girardeau gas.
Bose–Einstein condensates composed of a wide range of isotopes have been produced.[21]
Related experiments in cooling fermions rather than bosons to extremely low temperatures have created degenerate gases, where the atoms do not congregate in a single state due to the Pauli exclusion principle. To exhibit Bose–Einstein condensation, the fermions must "pair up" to form compound particles (e.g. molecules or Cooper pairs) that are bosons. The first molecular Bose–Einstein condensates were created in November 2003 by the groups of Rudolf Grimm at the University of Innsbruck, Deborah S. Jin at the University of Colorado at Boulder and Wolfgang Ketterle at MIT. Jin quickly went on to create the first fermionic condensate composed of Cooper pairs.[22]
In 1999, Danish physicist Lene Vestergaard Hau led a team from Harvard University which succeeded in slowing a beam of light to about 17 metres per second. She was able to achieve this by using a superfluid. Hau and her associates at Harvard University have since successfully made a group of condensate atoms recoil from a "light pulse" such that they recorded the light's phase and amplitude, which was recovered by a second nearby condensate, by what they term "slow-light-mediated atomic matter-wave amplification" using Bose–Einstein condensates: details of the experiment are discussed in an article in the journal Nature, 8 February 2007.[23]
Researchers in the new field of atomtronics use the properties of Bose–Einstein condensates when manipulating groups of identical cold atoms using lasers.[24]
Isotopes
The effect has mainly been observed on alkaline atoms which have nuclear properties particularly suitable for working with traps. As of 2010, using ultra-low temperatures of 10-7 K or below, Bose–Einstein condensates had been obtained for a multitude of isotopes, mainly of alkaline and alkaline earth atoms (7Li, 23Na, 39K, 41K, 85Rb, 87Rb, 133Cs, 52Cr, 40Ca, 84Sr, 86Sr, 88Sr, and 174Yb). Condensation research was finally successful even with hydrogen with the aid of special methods. In contrast, the superfluid state of the bosonic 4He at temperatures below 2.17 K is not a good example of Bose–Einstein condensation, because the interaction between the 4He bosons is too strong. Only 8% of the atoms are in the single-particle ground state near zero temperature, rather than the 100% expected of a true Bose–Einstein condensate.
The spin-statistics theorem of Wolfgang Pauli states that half-integer spins (in units of 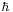 ) lead to fermionic behaviour, e.g., the Pauli exclusion principle forbidding that more than two electrons possess the same energy, whereas integer spins lead to bosonic behaviour, e.g., condensation of identical bosonic particles in a common ground state.
) lead to fermionic behaviour, e.g., the Pauli exclusion principle forbidding that more than two electrons possess the same energy, whereas integer spins lead to bosonic behaviour, e.g., condensation of identical bosonic particles in a common ground state.
The bosonic, rather than fermionic, behaviour of some of these alkaline gases appears odd at first sight since their nuclei have half-integer total spin. The bosonic behaviour arises from a subtle interplay of electronic and nuclear spins: at ultra-low temperatures and corresponding excitation energies, the half-integer total spin of the electronic shell and the half-integer total spin of the nucleus of the atom are coupled by a very weak hyperfine interaction. The total spin of the atom arising from this coupling is an integer value leading to the bosonic ultra-low temperature behaviour of the atom. The chemistry of the systems at room temperature is determined by the electronic properties, which is essentially fermionic, since at room temperature thermal excitations have typical energies much higher than the hyperfine values.
See also
References
- ^ Arora, C. P. (2001). Thermodynamics. Tata McGraw-Hill. p. 43. ISBN 0-074-62014-2. http://books.google.com/books?id=w8GhW3J8RHIC., Table 2.4 page 43
- ^ Ronald W. Clark, "Einstein: The Life and Times" (Avon Books, 1971) pp.408–9 ISBN 038001159X
- ^ "New State of Matter Seen Near Absolute Zero". NIST. http://physics.nist.gov/News/Update/950724.html.
- ^ Levi, Barbara Goss (2001). "Cornell, Ketterle, and Wieman Share Nobel Prize for Bose–Einstein Condensates". Search & Discovery. Physics Today online. Archived from the original on 2007-10-24. http://web.archive.org/web/20071024134547/http://www.physicstoday.org/pt/vol-54/iss-12/p14.html. Retrieved 2008-01-26.
- ^ Klaers, Jan; Schmitt, Julian; Vewinger, Frank; Weitz, Martin (2010). "Bose–Einstein condensation of photons in an optical microcavity". Nature 468 (7323): 545–548. Bibcode 2010Natur.468..545K. doi:10.1038/nature09567. PMID 21107426.
- ^ "Leiden University Einstein archive". Lorentz.leidenuniv.nl. 1920-10-27. http://www.lorentz.leidenuniv.nl/history/Einstein_archive/. Retrieved 2011-03-23.
- ^ S. T. Beliaev, Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 34, 418-432 (1958); ibid. 433-446 [Soviet Phys. JETP 3, 299 (1957)].
- ^ M. Schick, Phys. Rev. A 3, 1067 (1971); E. B. Kolomeisky and J. P. Straley, Phys. Rev. B 46, 11749 (1992); S. I. Shevchenko, Sov. J. Low Temp. Phys. 18, 223 (1992); E. B. Kolomeisky, T. J. Newman, J. P. Straley and X. Qi, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 1146 (2000); S. T. Chui and V. N. Ryzhov, Phys. Rev. A 69, 043607 (2004).
- ^ L. Salasnich, A. Parola, and L. Reatto, Phys. Rev. A 65, 043614 (2002).
- ^ A. V. Avdeenkov and K.G. Zloshchastiev, Quantum Bose liquids with logarithmic nonlinearity: Self-sustainability and emergence of spatial extent, J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 44 (2011) 195303 ArXiv:1108.0847.
- ^ a b "Eric A. Cornell and Carl E. Wieman — Nobel Lecture" (PDF). http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/laureates/2001/cornellwieman-lecture.pdf. Retrieved 2009-10-13.
- ^ C. C. Bradley, C. A. Sackett, J. J. Tollett, and R. G. Hulet (1995). "Evidence of Bose-Einstein Condensation in an Atomic Gas with Attractive Interactions". Physical Review Letters 75 (9): 1687–1690. Bibcode 1995PhRvL..75.1687B. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.75.1687. PMID 10060366.
- ^ Nikuni, T.; Oshikawa, M.; Oosawa, A.; Tanaka, H. (1999). "Bose–Einstein Condensation of Dilute Magnons in TlCuCl3". Physical Review Letters 84 (25): 5868. arXiv:cond-mat/9908118. Bibcode 2000PhRvL..84.5868N. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.84.5868. PMID 10991075.
- ^ Demokritov, S.O.; Demidov, VE; Dzyapko, O; Melkov, GA; Serga, AA; Hillebrands, B; Slavin, AN (2006). "Bose–Einstein condensation of quasi-equilibrium magnons at room temperature under pumping". Nature 443 (7110): 430–433. Bibcode 2006Natur.443..430D. doi:10.1038/nature05117. PMID 17006509.
- ^ Ralph Baierlein (1999). Thermal Physics. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521658381. http://books.google.com/?id=fqUU71spbZYC&printsec=frontcover.
- ^ Becker C. et al. (2008). "Oscillations and interactions of dark and dark–bright solitons in Bose–Einstein condensates". Nature Physics 4 (6): 496–501. Bibcode 2008NatPh...4..496B. doi:10.1038/nphys962.
- ^ van Putten, M.H.P.M.. "Pair condensates produced in bosenovae". Physics Letters A, 374, 3346 (2010). http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2010PhLA..374.3346V.
- ^ Axel Gorlitz. "Interference of Condensates (BEC@MIT)". Cua.mit.edu. http://cua.mit.edu/ketterle_group/Projects_1997/Interference/Interference_BEC.htm. Retrieved 2009-10-13.
- ^ Zachary Dutton, Naomi S. Ginsberg, Christopher Slowe, and Lene Vestergaard Hau (2004). "The art of taming light: ultra-slow and stopped light". Europhysics News 35 (2): 33. Bibcode 2004ENews..35...33D. doi:10.1051/epn:2004201. http://www.europhysicsnews.org/articles/epn/pdf/2004/02/epn04201.pdf.
- ^ "From Superfluid to Insulator: Bose-Einstein Condensate Undergoes a Quantum Phase Transition". Qpt.physics.harvard.edu. http://qpt.physics.harvard.edu/qptsi.html. Retrieved 2009-10-13.
- ^ "Ten of the best for BEC — physicsworld.com". Physicsweb.org. http://physicsweb.org/articles/world/18/6/1. Retrieved 2009-10-13.
- ^ "Fermionic condensate makes its debut — physicsworld.com". Physicsweb.org. http://physicsweb.org/articles/news/8/1/14/1. Retrieved 2009-10-13.
- ^ Naomi S. Ginsberg; Sean R. Garner; Lene Vestergaard Hau (8 February 2007). "Coherent control of optical information with matter wave dynamics". Nature 445 (7128): 623–626. doi:10.1038/nature05493. PMID 17287804.
- ^ P. Weiss (12 February 2000). "Atomtronics may be the new electronics". Science News Online 157: 104. http://www.sciencenews.org/view/generic/id/69786. Retrieved 2011-02-12.
Further reading
- Bose, S. N. (1924). "Plancks Gesetz und Lichtquantenhypothese". Zeitschrift für Physik 26: 178. Bibcode 1924ZPhy...26..178B. doi:10.1007/BF01327326.
- Einstein, A. (1925). "Quantentheorie des einatomigen idealen Gases". Sitzungsberichte der Preussischen Akademie der Wissenschaften 1: 3.,
- Landau, L. D. (1941). "The theory of Superfluity of Helium 111". J. Phys. USSR 5: 71–90.
- L. Landau (1941). "Theory of the Superfluidity of Helium II". Physical Review 60 (4): 356–358. Bibcode 1941PhRv...60..356L. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.60.356.
- M.H. Anderson, J.R. Ensher, M.R. Matthews, C.E. Wieman, and E.A. Cornell (1995). "Observation of Bose–Einstein Condensation in a Dilute Atomic Vapor". Science 269 (5221): 198–201. Bibcode 1995Sci...269..198A. doi:10.1126/science.269.5221.198. JSTOR 2888436. PMID 17789847.
- C. C. Bradley, C. A. Sackett, J. J. Tollett, and R. G. Hulet (1995). "Evidence of Bose-Einstein Condensation in an Atomic Gas with Attractive Interactions". Physical Review Letters 75 (9): 1687–1690. Bibcode 1995PhRvL..75.1687B. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.75.1687. PMID 10060366..
- C. Barcelo, S. Liberati and M. Visser (2001). "Analogue gravity from Bose–Einstein condensates". Classical and Quantum Gravity 18 (6): 1137–1156. arXiv:gr-qc/0011026. Bibcode 2001CQGra..18.1137B. doi:10.1088/0264-9381/18/6/312.
- P.G. Kevrekidis, R. Carretero-Gonzlaez, D.J. Frantzeskakis and I.G. Kevrekidis (2006). "Vortices in Bose–Einstein Condensates: Some Recent Developments". Modern Physics Letters B 5 (33). http://nlds.sdsu.edu/.
- K.B. Davis, M.-O. Mewes, M.R. Andrews, N.J. van Druten, D.S. Durfee, D.M. Kurn, and W. Ketterle (1995). "Bose–Einstein condensation in a gas of sodium atoms". Physical Review Letters 75 (22): 3969–3973. Bibcode 1995PhRvL..75.3969D. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.75.3969. PMID 10059782..
- D. S. Jin, J. R. Ensher, M. R. Matthews, C. E. Wieman, and E. A. Cornell (1996). "Collective Excitations of a Bose–Einstein Condensate in a Dilute Gas". Physical Review Letters 77 (3): 420–423. Bibcode 1996PhRvL..77..420J. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.420. PMID 10062808.
- M. R. Andrews, C. G. Townsend, H.-J. Miesner, D. S. Durfee, D. M. Kurn, and W. Ketterle (1997). "Observation of interference between two Bose condensates". Science 275 (5300): 637–641. doi:10.1126/science.275.5300.637. PMID 9005843..
- Eric A. Cornell and Carl E. Wieman (1998). "The Bose-Einstein Condensate". Scientific American 278 (3): 40–45. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0398-40.
- M. R. Matthews, B. P. Anderson, P. C. Haljan, D. S. Hall, C. E. Wieman, and E. A. Cornell (1999). "Vortices in a Bose–Einstein Condensate". Physical Review Letters 83 (13): 2498–2501. arXiv:cond-mat/9908209. Bibcode 1999PhRvL..83.2498M. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.83.2498.
- E.A. Donley, N.R. Claussen, S.L. Cornish, J.L. Roberts, E.A. Cornell, and C.E. Wieman (2001). "Dynamics of collapsing and exploding Bose–Einstein condensates". Nature 412 (6844): 295–299. arXiv:cond-mat/0105019. Bibcode 2001Natur.412..295D. doi:10.1038/35085500. PMID 11460153.
- A. G. Truscott, K. E. Strecker, W. I. McAlexander, G. B. Partridge, and R. G. Hulet (2001). "Observation of Fermi Pressure in a Gas of Trapped Atoms". Science 291 (5513): 2570–2572. Bibcode 2001Sci...291.2570T. doi:10.1126/science.1059318. PMID 11283362.
- M. Greiner, O. Mandel, T. Esslinger, T. W. Hänsch, I. Bloch (2002). "Quantum phase transition from a superfluid to a Mott insulator in a gas of ultracold atoms". Nature 415 (6867): 39–44. Bibcode 2002Natur.415...39G. doi:10.1038/415039a. PMID 11780110..
- S. Jochim, M. Bartenstein, A. Altmeyer, G. Hendl, S. Riedl, C. Chin, J. Hecker Denschlag, and R. Grimm (2003). "Bose–Einstein Condensation of Molecules". Science 302 (5653): 2101–2103. Bibcode 2003Sci...302.2101J. doi:10.1126/science.1093280. PMID 14615548.
- Markus Greiner, Cindy A. Regal and Deborah S. Jin (2003). "Emergence of a molecular Bose−Einstein condensate from a Fermi gas". Nature 426 (6966): 537–540. Bibcode 2003Natur.426..537G. doi:10.1038/nature02199. PMID 14647340.
- M. W. Zwierlein, C. A. Stan, C. H. Schunck, S. M. F. Raupach, S. Gupta, Z. Hadzibabic, and W. Ketterle (2003). "Observation of Bose–Einstein Condensation of Molecules". Physical Review Letters 91: 250401. arXiv:cond-mat/0311617. Bibcode 2003PhRvL..91y0401Z. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.91.250401. PMID 14754098.
- C. A. Regal, M. Greiner, and D. S. Jin (2004). "Observation of Resonance Condensation of Fermionic Atom Pairs". Physical Review Letters 92 (4): 040403. arXiv:cond-mat/0401554. Bibcode 2004PhRvL..92d0403R. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.040403. PMID 14995356.
- C. J. Pethick and H. Smith, Bose–Einstein Condensation in Dilute Gases, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2001.
- Lev P. Pitaevskii and S. Stringari, Bose–Einstein Condensation, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 2003.
- Mackie M, Suominen KA, Javanainen J., "Mean-field theory of Feshbach-resonant interactions in 85Rb condensates." Phys Rev Lett. 2002 Oct 28;89(18):180403.
External links
- Bose-Einstein Condensation 2009 Conference Bose-Einstein Condensation 2009 - Frontiers in Quantum Gases
- BEC Homepage General introduction to Bose–Einstein condensation
- Nobel Prize in Physics 2001 - for the achievement of Bose–Einstein condensation in dilute gases of alkali atoms, and for early fundamental studies of the properties of the condensates
- Physics Today: Cornell, Ketterle, and Wieman Share Nobel Prize for Bose–Einstein Condensates
- Bose–Einstein Condensates at JILA
- Atomcool at Rice University
- The Bose–Einstein Condensate at Utrecht University, the Netherlands
- Alkali Quantum Gases at MIT
- Atom Optics at UQ
- Einstein's manuscript on the Bose–Einstein condensate discovered at Leiden University
- The revolution that has not stopped PhysicsWeb article from June 2005
- Bose–Einstein condensate on arxiv.org
- Bosons - The Birds That Flock and Sing Together
- Oxford Experimental BEC Group.
- Cambridge University Cold Atoms Group.
- Easy BEC machine - information on constructing a Bose–Einstein condensate machine.
- Verging on absolute zero - Cosmos Online
- Lecture by W Ketterle at MIT in 2001
- Bose-Einstein Condensation at NIST - NIST resource on BEC
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
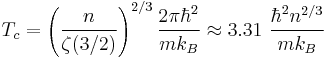
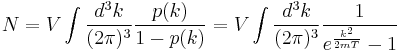
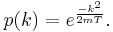
![E=\int
d\vec{r}\left[\frac{\hbar^2}{2m}|\nabla\psi(\vec{r})|^2%2BV(\vec{r})|\psi(\vec{r})|^2%2B\frac{1}{2}U_0|\psi(\vec{r})|^4\right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/28acaa0d6f6c112ca9b3e5e5ac53d33b.png)